- through unwashed hands;
- After contact with animals;
- by undercooked meat and fish;
- Insects are also often the source of worm infections because they carry eggs on their legs;
- Unwashed vegetables and fruits;
- Dirty water accidentally swallowed while swimming in open water.
Worm infection in children, symptoms
- Loss of appetite, pale facial skin, and dark circles under the eyes.
- Restless sleep; sometimes children may grind their teeth while sleeping.
- Headache, dizziness, drowsiness, and weakness occur.
- Sometimes, visible worms are present in a child's stool.
- Your baby's genital area and anus may become itchy.
- Disturbances in the digestive system occur, constipation may be replaced by diarrhea, abdominal pain and nausea are observed.
- There may be changes in general blood count indicators, namely decreased hemoglobin, increased eosinophils and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- The vital activity of worms becomes the cause of systemic poisoning, manifested by the appearance of allergic reactions, urticaria and atopic dermatitis.
- Body temperature rises for no apparent reason.
- Persistent itching can lead to inflammation of the genital mucosa.
- Worms not only poison the child's body with the products of their life activities, but also actively consume vitamins and minerals that the child's body greatly needs, which often leads to vitamin deficiencies and a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
Folk remedies against worms
- Garlic enema. Garlic is nature's antiseptic for humans; it is also useful against worms. Mix a cup of milk with a head of chopped garlic, bring the mixture to a boil, then cool and strain through a double layer of gauze. In the evening, give the child an enema with the milk received, take a third of the medicine, and treat the child in this way for at least a week.
- Chamomile soup. Another natural antiseptic used to treat a variety of ailments. To prepare a decoction, take a tablespoon of dried chamomile herb, pour it with boiling water, wait for it to cool and let the child drink it throughout the day instead of water or tea. The duration of treatment is 5 days.
- Onion Remedy. Chop a small onion, add milk, boil the resulting mixture, then cool and strain. The resulting product is given to infants in 100 ml doses for three consecutive days.
Causes of helminthiasis
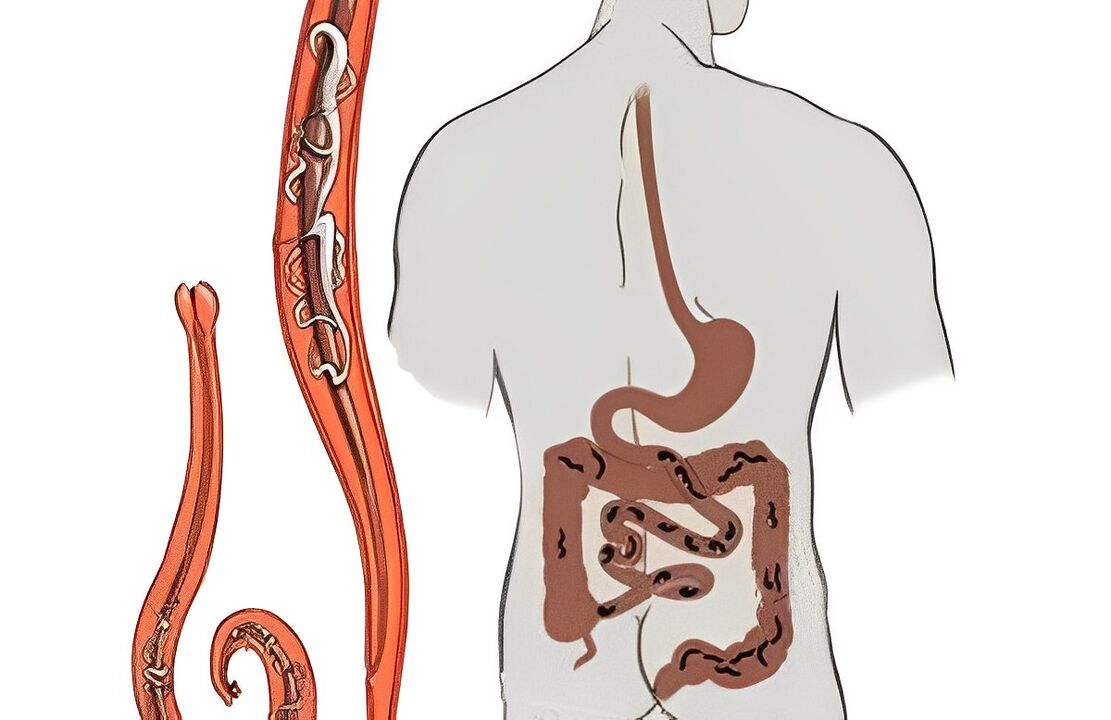
Symptoms of worms
- The temperature rises. After taking anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs, the temperature can rise sharply to 38°C and then drop briefly. Sometimes the high temperatures last for 2-3 months.
- Dull or tingling pain in the stomach, frequent bowel movements (diarrhea or constipation), and nausea.
- Itching in the anal area, worse at night.
- Frequent colds or respiratory illnesses – After being infected with worms, immunity can be reduced.
- Loss or increase of appetite, sudden weight loss.
- Bronchospasm, cough, shortness of breath, other breathing disorders, pale skin and mucous membranes.
- Itchy rash.
- Insomnia, frequent headaches, anxiety, irritability, depression.
- Joint and muscle pain.
- Inflammation, swollen lymph nodes.
- edema.
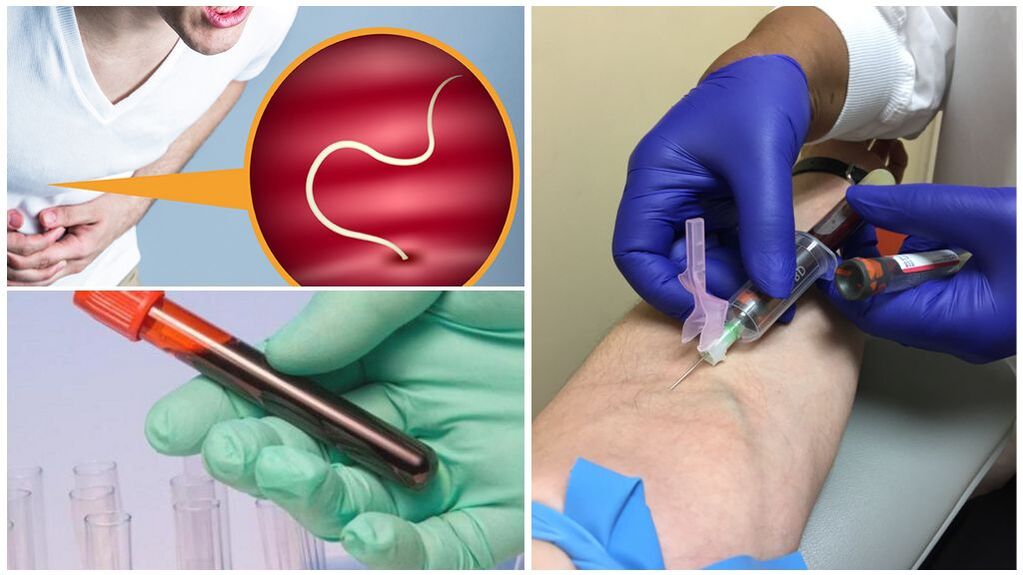
diagnosis
- Stool analysis. Allows you to accurately detect the presence of common parasites in your body. However, some of them only lay eggs during certain stages of their life cycle, so several surveys every 3-4 days are recommended.
- General clinical blood tests. It does not indicate the presence of larvae, eggs, adult worms, but provides a lot of information about the intensity of the inflammatory process, the number of white blood cells, etc.
- Biochemical analysis. Provides detailed information on protein metabolism, identifies abnormal losses or increases in protein synthesis, and allows one to rule out or suspect infection with certain helminths.
- Analysis of liver function indicators (bilirubin, pancreatic α-amylase, alkaline phosphatase, AST, ALT). Diagnosis of the liver and pancreas suggested helminth infection.
- Urinalysis, glomerular filtration blood test. They provide doctors with information about the condition of the kidneys and the potential for parasites to damage the kidneys.
Which doctors should I contact?
treat
complication
Classification of parasites
symptom
- Irritability, disturbed sleep, decreased perseverance and concentration, frequent hysteria and anger;
- Increased appetite associated with active weight loss;
- Digestive symptoms - diarrhea, constipation, nausea, pain in the right rib;
- dizziness and headache;
- food allergy;
- nasal discharge;
- Reproductive system diseases and infections;
- brittle nails/hair;
- Nocturnal urination;
- molar;
- Enlargement of liver, spleen, and lymph nodes;
- Temperatures rise, sometimes as high as 38 degrees;
- experiencing discomfort and weakness;
- Development of respiratory diseases - pneumonia, bronchitis and bronchial asthma;
- pressure drops;
- The development of gastrointestinal symptoms - constipation, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, painful uterine contractions;
- Afraid of light;
- nightmares at night;
- Dry cough - phlegm that is orange and speckled with blood.
diagnosis
- Blood tests - showing anemia, hemoglobin and eosinophil levels;
- Parasite analysis - in 99% of cases it helps to detect helminthiasis, in most cases it helps to accurately determine the type (biological material used for research - blood from veins);
- Check the feces - there may be no eggs in the feces. Even if there is an infection, make sure there are worms. This diagnosis needs to be done three times and takes time;
- Smear test – particularly effective for pinworm infections as the eggs are found just outside the anus;
- Stool analysis for the presence of dysbiosis;
- If infection of internal organs, not just the gastrointestinal tract is suspected - CT, X-ray, ultrasound.
treat
- The first process kills already developed individuals;
- A second course of treatment helps deal with larvae and eggs (given two weeks after the first course).
Consequences of untreated parasitic infection
- Increased inflammation in appendicitis;
- epileptic seizures;
- Various types of visual impairment;
- Allergic reaction with profuse nasal discharge;
- Developmentally lags behind peers;
- Sexually transmitted infections, the most common among girls is vulvovaginitis;
- Various types of pulmonary manifestations, including bronchial asthma;
- In difficult cases - damage to the brain and heart.
prevention
- Maintain hygiene - wash hands and bathe children regularly;
- Regular care of toys - washing and cleaning (all toys must be disinfected after diagnosis);
- Cut your nails as often as possible and clean them daily;
- Iron clothes after washing;
- Break bad habits – thumb sucking, pen sucking, nail biting;
- Drink only boiled water and explain why;
- Avoid swimming in natural bodies of water;
- Use insect repellent (insects often carry eggs) to eliminate any insects that enter the house;
- Check pets regularly for parasites;
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly and heat-treat meat and fish adequately.